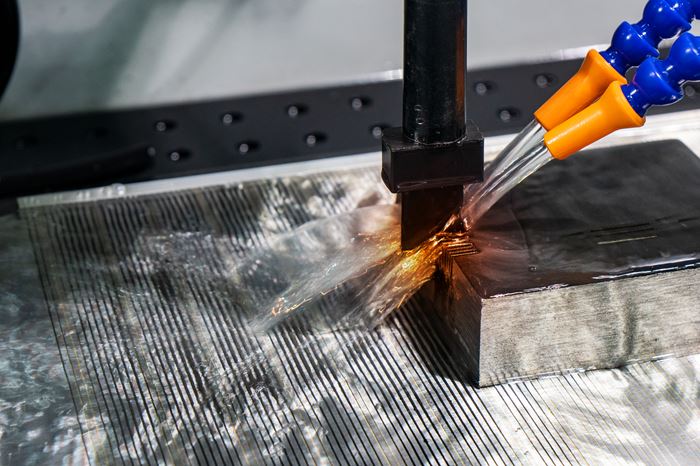
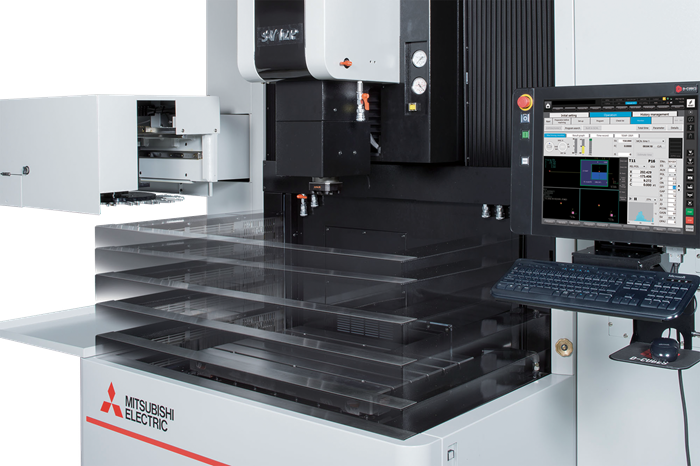
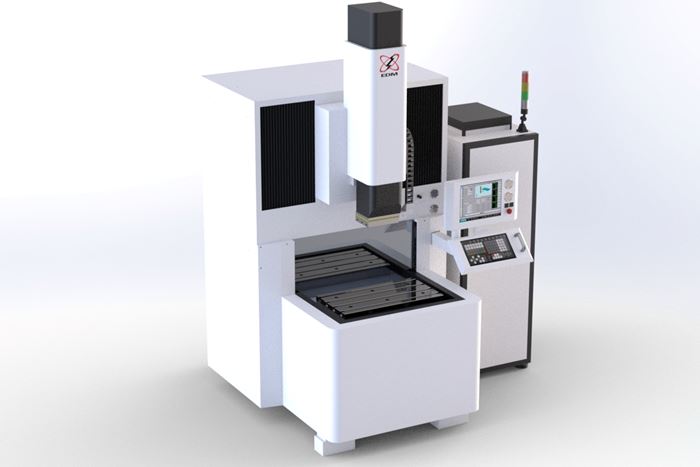
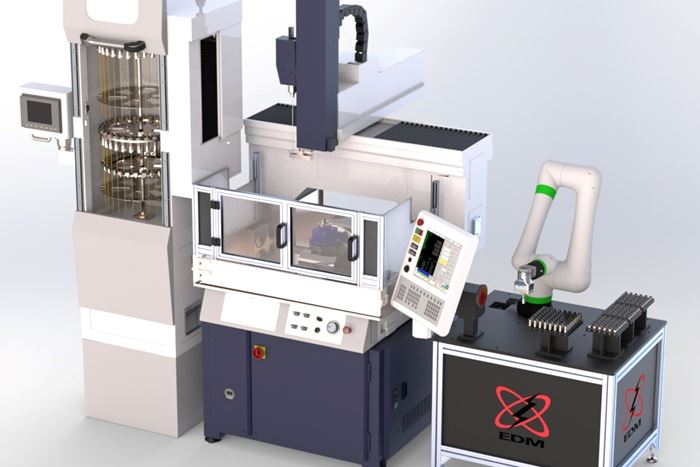
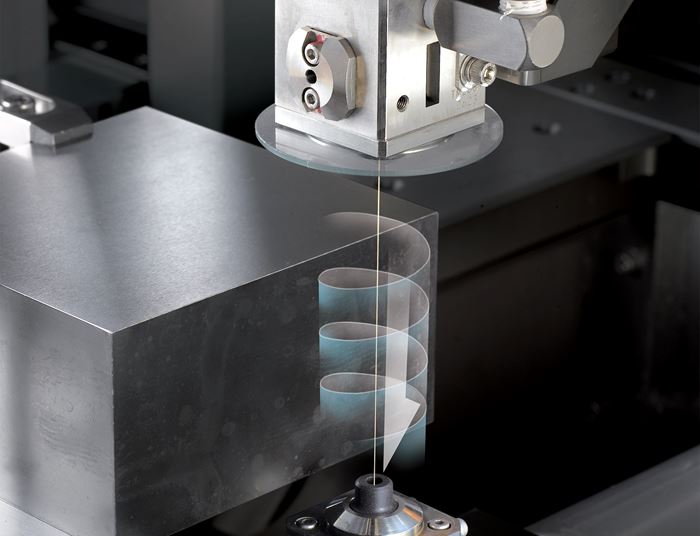
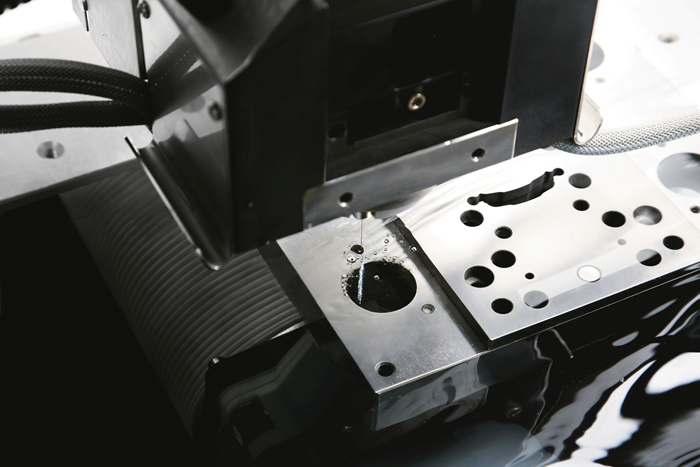
EDM, or electrical discharge machining, is capable of machining complex shapes in hard materials. The process includes an electrode and a workpiece, both submerged in dielectric fluid. Electrical current flows between the workpiece and electrode, repeatedly creating tiny plasma zones that instantaneously melt and remove the material. The electrode in EDM takes different forms. Wire EDM machines use a thin wire to cut. Ram EDM machines, or “die sinkers,” use electrodes that are custom machined into 3D shapes. The EDM process produces a cavity in the part that is the opposite or female version of the “male” electrode form. Similar to the ram EDM machine is the small-hole EDM machine, or “hole popper.” On this machine, the electrode is a cylinder used to machine a hole.
Five Reminders For Machining Graphite
Graphite machining can be a tricky business, so keeping certain issues top of mind is vital to productivity and profitability.
EDM: Essential Reading
MC Machinery to Showcase EDMs and More
Eastec 2021: MC Machinery will highlight two EDM machines, a five-axis VMC and more in booth 1426.
Machining 101: What is Electrical Discharge Machining?
Electrical discharge machining, or EDM, is a non-contact form of machining that projects sparks from an electrode or wire to vaporize material of any hardness.
Methods Machine Tools Adds New FANUC EDM Models
Methods Machine Tools Inc. added the next generation of the FANUC RoboCut series to its line of wire electrical discharge machining (EDM) products.
New Machining Centers Improve Moldmaking Workflow
Westminster Tool has shifted the workflow in its moldmaking department to incorporate high-speed five-axis and, as a result, cut lead times and reduce the need for wire EDM.
Mitsui Seiki Installs First Blue Arc Machine
Mitsui Seiki has installed what it says is the first Blue Arc-using machine tool. Blue Arc uses a multiple-point discharge event for material removal, whereas EDM uses a single-point discharge.

FAQ: EDM
What is EDM?
Electrical discharge machining, or EDM, is a non-contact process that can machine parts regardless of their hardness. It involves placing an electrode or wire and an electrically conductive workpiece into a circulating dielectric fluid. The fluid acts as an insulator until a specific spark gap and voltage ionizes it and enables a spark to travel to the workpiece.
Using a CNC, the operator moves the electrode or wire as needed and rapidly turns the current on and off. This accommodates the flushing of molten material (often called “swarf”) from the workpiece.
Source: Machining 101: What is Electrical Discharge Machining?
What are the two types of EDM machines?
The two main types of EDM machines are sinker EDM machines and wire EDM machines.
Source: Machining 101: What is Electrical Discharge Machining?
What is sinker EDM?
Sinker EDM uses an electrode as its “cutting” tool, with the shape of the electrode serving as a mirrored, slightly smaller image of the finished form it will produce in the workpiece. The electrode makes one spark at a time — but the frequency of the current means the tool could produce anywhere between 500 and 30,000 sparks per second.
Electrodes for sinker EDM are typically either copper or graphite.
Source: Machining 101: What is Electrical Discharge Machining?
What is wire EDM?
Wire EDM feeds a strand of wire from a supply spool to the workpiece via a wire drive system. The wire is energized by electrical contacts and passes through the workpiece at a specific velocity determined by the operation at hand. A stream or bath of deionized water surrounds the wire, and sparks are continuously emitted along the length of the wire. Rollers pinch the wire and provide tension, while guides above and below the workpiece position the wire on its path — helping it to achieve complex shapes on the workpiece.
The wires used in this process commonly have diameters of 0.010 to 0.012 inch, with finer wires at 0.001 to 0.004 inch. The material of the wires also holds great influence over the operation’s success, as hard wires that have insufficient tensile strength for an operation are liable to break under sudden shock. Softer wires prove more desirable for high-taper cutting operations.
Source: Machining 101: What is Electrical Discharge Machining?
What is swarf?
During the EDM process, the operator moves the electrode or wire as needed and rapidly turns the current on and off. This accommodates the flushing of molten material (often called “swarf” or “chips”) that is removed from the workpiece.
Source: Machining 101: What is Electrical Discharge Machining?

EDM Suppliers
Automation Adds Capacity to Capability for Low-Volume Work
Investment in machining technology has facilitated growth and diversification at Reich Tool & Design. Now, flexible automation allows the shop to get more out of its machines despite a shortage of skilled workers.
#topshops
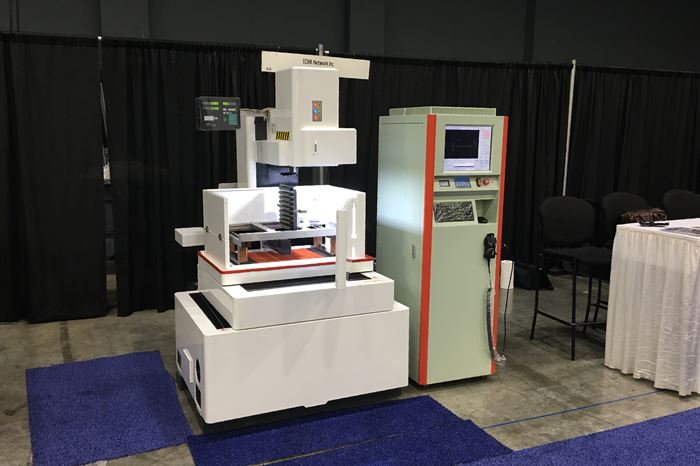
Rapid Metal Parts Removal With EDM Network Inc.'s New EDM
According to EDM Network Inc., the Fast Wire EDM is capable of cutting speeds that are two to three times faster than traditional wire EDMs.
Five Reminders For Machining Graphite
Graphite machining can be a tricky business, so keeping certain issues top of mind is vital to productivity and profitability.
MC Machinery to Showcase EDMs and More
Eastec 2021: MC Machinery will highlight two EDM machines, a five-axis VMC and more in booth 1426.
Machining 101: What is Electrical Discharge Machining?
Electrical discharge machining, or EDM, is a non-contact form of machining that projects sparks from an electrode or wire to vaporize material of any hardness.
#Basics
Methods Machine Tools Adds New FANUC EDM Models
Methods Machine Tools Inc. added the next generation of the FANUC RoboCut series to its line of wire electrical discharge machining (EDM) products.
New Machining Centers Improve Moldmaking Workflow
Westminster Tool has shifted the workflow in its moldmaking department to incorporate high-speed five-axis and, as a result, cut lead times and reduce the need for wire EDM.
#casestudy