The broad category of “cutting tools” includes all of the consumable tooling involved in milling, drilling, turning and other lathe and machining center operations.
Drills, end mills, taps, reamers and inserts are all included here. Consumable tooling used on certain other types of machine tools is included here as well. Also found here are toolholders and closely related accessories such as angle heads. Supplier pages, FAQs related to cutting and cutting tools can be found here, as well as essential reading on the topic and all of the latest Modern Machine Shop cutting tools coverage.
Selecting a Thread Mill That Matches Your Needs
Threading tools with the flexibility to thread a broad variety of holes provide the agility many shops need to stay competitive. They may be the only solution for many difficult materials.
Cutting Tools : Essential Reading
Emuge-Franken's New Drill Geometry Optimizes Chipbreaking
PunchDrill features patent-pending geometry with a chipbreaker that produces short chips to control machining forces.
Allied Machine and Engineering Offers New Sizes of Thread Milling Tools
The AccuThread T3 thread mill line is now available in larger UN and ISO sizes up to 1"-8" and M24 × 3.0.
Greenleaf Solid Ceramic End Mills Maximize Material Removal
Eastec 2023: Xsytin-360 end mills feature a four-flute design designed to minimize cutting forces, reduce vibrations and optimize tool life.
Emuge-Franken Solid Carbide Drills Withstand Shock, Chipping
The MultiDrill’s TiAlN-T63 coating uses nano-layer technology with surface hardness, providing reduced friction at high temperatures.
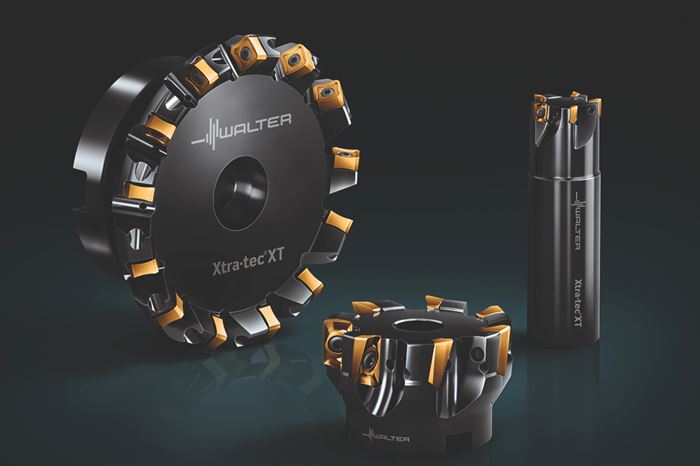
Walter Milling Inserts Feature PCD Cutting Edges
The PCD inserts are suitable for milling a variety of nonferrous workpiece materials, such as aluminum, aluminum-silicon alloys, magnesium, magnesium-based alloys, plastics and fiber-reinforced plastics.

FAQ: Cutting Tools
Why is through-tool coolant valuable, and why are shops are seeing greater need for it?
Getting coolant to the cutting edge is critical for any manufacturing application. It helps in cooling the cutting zone, provides very needed lubrication, and can assist in breaking a chip. Many times, external lines are used to splash coolant near the work zone. Long Chips can easily interfere with this delivery method, possibly knocking the lines out of the way. Additionally, when tools need to be changed or indexed coolant lines might be moved for better access to the tool. Then when the line is put back it is never the same as it previously was. Often times there is a give-and-take methodology used to cover areas being machined with this coolant, so all tools get some cooling, but none of them get ideal cooling. A coolant-through tool allows pinpoint accuracy with a specific direction of coolant pointed exactly at the cutting zone.
Through-tool coolant is available on cutters that couldn't offer it before. What has changed in the technology of tool manufacturing to make this possible?
There’s been a big change is the ability to drill small-diameter holes very deep and do this in a production atmosphere. Part of this comes from the drilling machines being able to reach the necessary speeds and holders that provide superior clamping and runout. The other part comes from tools designed specifically for this drilling application.
On a coolant-through tool, material could be added in areas that may need additional strength, allowing for the intersecting coolant ports to be drilled accordingly.
What aspect of tool engineering is responding to greater cutting speed?
Machines and tools seem to have a back-and-forth dance in terms of which is leading. Coatings continue to evolve, with more layers, and different material being used. This is something all tool manufactures are playing with on some level. The changes in coating technology is somewhat more limited, and not as many are playing in this arena. One process that comes to mind is “HiPIMS,” or high-power impulse magnetron sputtering. This process uses microsecond timing of extreme-power pulses. This allows the metal to ionize to nano size particles to be deposited on the tools. This process allows for greater adhesion and coating hardness, while maintaining great lubricity. Additionally, this process has greatly reduced compressive stresses. This reduction allows for smaller edge preps to be used, thus resulting in sharper tools.
Why is diamond used as an industrial cutting tool?
Developments in polycrystalline diamond (PCD) and cubic boron nitride (CBN) have allowed these materials to improve in ways that make them more versatile and cost-effective. Meanwhile, the machining speed and tool life of these tools continue to take machining processes to levels of performance where carbide cannot go.
Through long tool life and fast cutting parameters, the tools increase machine capacity by reducing the frequency of tool replacements and allowing machines to make parts at a greater rate. Meanwhile, the tooling increasingly figures into expert solutions tailored to more demanding applications in various industries.
Source: The New Rules of Cutting Tools - Rule #3: Diamond Shouldn't Be Rare
What are cutting tools made of?
Polycrystalline diamond (PCD), cubic boron nitride (CBN), ceramic, high-speed steel (HHS), cemented carbide or cermet.
Sources: What's Happening With Cutting Tools

Cutting Tools Suppliers
Narrow by Cutting Tools Category
- Abrasive Compounds & Slurries
- Arbors (for Cutters)
- Boring Tools
- Boring Tools & Heads for Machining Centers
- Boring Tools for Turning Machines
- Broaching Tools
- Buffing & Polishing Supplies
- Burnishing Tools (Roller)
- Burnishing, Honing & Lapping Tools
- Chamfering Tools
- Cold Heading Tools
- Collets for Toolholding
- Collets, Solid & Master
- Counterbores/Countersinks
- Cut-Off Tools/Attachments
- Deburring Tools (Machine Tool Spindle-Mounted)
- Diamond Tools
- Die & Mold Components
- Drill Bushings
- Drill Chucks
- Drills
- Drilling Heads/Attachments
- End Mills
- Facing Tools/Heads
- Endworking Tools
- Form Tools
- Gear Cutting Tools
- Gear Rolling Tools
- Grinding Wheel Dressing Units
- Grinding Wheels & Belts
- Grooving Tools
- Gundrills
- Honing & Lapping Tools
- Inserts, Indexable (Carbide, etc.) & Tool Inserts
- Knurling Tools
- Key Seating Tools
- Marking Tools
- Mass Finishing Media & Compounds
- Milling Cutters
- Milling Heads/Attachments
- Protective Sleeves & Coatings (for Cutting Tools)
- Punching Tools/Dies
- Reamers
- Retention Knobs
- Serration Tooling
- Saw Blades
- Shaving Tools
- Shear Blades
- Slotting Saws
- Spline Inserts
- Spline Rolling Tools
- Tap Drivers & Attachments
- Taps
- Thread Chasers
- Thread Milling Cutters
- Thread Rolls & Dies
- Thread Whirling Tools
- Threading Tools
- Threading Tools - Cutting
- Threading Tools - Forming
- Tool Blanks
- Tool Condition Monitoring Systems
- Tool Conditioning Equipment
- Tool Presetters
- Tool Repair, Coating & Treatment Services
- Tool Storage & Handling Systems
- Toolholders
- Tooling Materials, Carbides
- Tooling Materials, Ceramics
- Tooling Systems, Modular and/or Quick-Change
Grooving Attachment Streamlines Operation by 75%
A grooving attachment enabled Keselowski Advanced Manufacturing to reduce cycle times by over 45 minutes on a high-value, high-nickel part feature.
Sandvik Coromant Turning Tools Enable Y-Axis Turning
The company has developed two new tools to support Y-axis turning: CoroTurn Prime and the CoroPlex YT twin-tool.
Emuge-Franken's New Drill Geometry Optimizes Chipbreaking
PunchDrill features patent-pending geometry with a chipbreaker that produces short chips to control machining forces.
Allied Machine and Engineering Offers New Sizes of Thread Milling Tools
The AccuThread T3 thread mill line is now available in larger UN and ISO sizes up to 1"-8" and M24 × 3.0.
Greenleaf Solid Ceramic End Mills Maximize Material Removal
Eastec 2023: Xsytin-360 end mills feature a four-flute design designed to minimize cutting forces, reduce vibrations and optimize tool life.
Emuge-Franken Solid Carbide Drills Withstand Shock, Chipping
The MultiDrill’s TiAlN-T63 coating uses nano-layer technology with surface hardness, providing reduced friction at high temperatures.
Walter Milling Inserts Feature PCD Cutting Edges
The PCD inserts are suitable for milling a variety of nonferrous workpiece materials, such as aluminum, aluminum-silicon alloys, magnesium, magnesium-based alloys, plastics and fiber-reinforced plastics.